This Tutorial will help u gain confidence in MySQL. Just make sure that u will follow each steps. If you find any problem, just leave comment,I will reply asap.
Packages required to be installed
DEVAst02:~ # rpm -qa|grep mysql
mysql-shared-5.0.26-12.18
mysql-client-5.0.26-12.18
mysql-devel-5.0.26-12.18
mysql-5.0.26-12.18
perl-DBD-mysql-3.0002-15.2
Default config file /etc/my.conf
Post Installation:
1> Create Password for root user
Admin user id: root
Default password: blank
The first task is to assign a password:
| [prompt]$ mysqladmin -u root password 'new-password' |
Note: the following SQL commands will also work:
| mysql> USE mysql; mysql> UPDATE user SET Password=PASSWORD('new-password') WHERE user='root'; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; |
2> Delete blank user (Security Issue)
MySql has blank user for test purpose. It should be removed.
DEVAst02:~ # mysql -h localhost -u -p
Running above command gives access to mysql. So, it needs to be deleted
mysql> show databases;
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> SELECT User,Password,Host from user;
mysql> DELETE FROM user WHERE User=' ';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Some Fundamental Operations:
1> Create Database, create table, add entries, update entries, delete entires; drop table and drop database;
DEVAst02:~ # mysql -h localhost -u root -p
mysql> show databases;
mysql> create database asterisk;
mysql> show databases;
mysql> use asterisk;
mysql> show tables;
mysql> create table Records (Number char(20),Name char(20), email varchar(40));
mysql> show tables;
mysql> describe Records;
mysql> INSERT INTO Records(Number,Name,email) VALUES('25962','Dev Shah','dev.shah@something.edu');
mysql> SELECT * FROM Records;
mysql> UPDATE Records SET Name='Deven Shah' WHERE Number='25962';
mysql> SELECT * FROM Records;
mysql> DELETE FROM Records WHERE Number='25962';
mysql> drop table Records;
mysql> drop database asterisk;
Security:
Security and database access is controlled by the GRANT tables. Access to connect to the database and access to process the transaction (table and column access, etc.) are both required. Privileges are searched in the following order:
user table
db and host table
tables_priv
columns_priv
DEVAst02:~ # mysql -h localhost -u root -p
mysql> show databases;
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> show tables;
Mysql> SELECT * FROM User;
Use the user table to grant connection privileges to database by a user (host, user name and password). Grant database and table access for transaction access. i.e. grant "SELECT", "UPDATE", "CREATE", "DELETE", "ALTER" etc. permission for database, table, field (columns) or database server access.
Add a user and grant the access:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE asteriskdb;
mysql> USE mysql;
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_mysql |
+-----------------+
| columns_priv |
| db |
| func |
| host |
| tables_priv |
| user |
+-----------------+
mysql> INSERT INTO user (Host, User, Password, Select_priv) VALUES ('', 'asteriskuser', password('redhat'), 'Y');
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; - Required each time one makes a change to the GRANT table
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON asteriskdb.* TO asteriskuser;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; - Required each time one makes a change to the GRANT table
mysql> quit
Now try:
DEVAst02:~ # mysql -h localhost -u asteriskuser -predhat
mysql> use mysql;
ERROR 1044 (42000): Access denied for user 'asteriskuser'@'%' to database 'mysql'
mysql> use asteriskdb;
Database changed
Since you are accessing mysql as asteriskuser,you are granted only to access asteriskdb.
If you need to grant access to all databases, you should Grant
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO asteriskuser;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Assignment: Create a user 'dbreader' with password 'redhat' that has read-only permission on database 'phones'.
Step1: Create user
msyql>CREATE USER 'dbreader'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'redhat';
Step2: Grant rights for read-only
mysql>GRANT SELECT ON phones.* TO 'dbsreader'@'%';
[Note: Granting SELECT command is enough for READ operation]
Now you should be able to access 'phones' database from any machine using user 'dbreader'.
For More: http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/LinuxTutorialMySQL.html
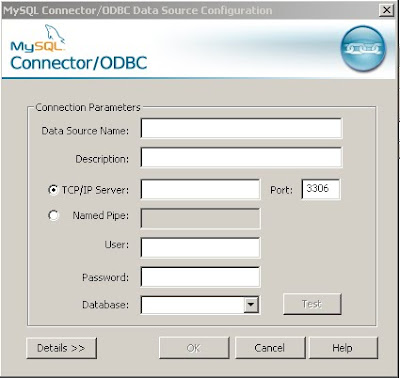 Populate the credentials. You can give any name for "Data Source Name". Let's say 'myData'. Specify you MySQL server IP address, username, password and the database. Click on 'Test' and see if the connector can connect to your MySQL database or not. If not, check if you can ping you MySQL box and check if the user is granted privilege to access locally or remotely.
Populate the credentials. You can give any name for "Data Source Name". Let's say 'myData'. Specify you MySQL server IP address, username, password and the database. Click on 'Test' and see if the connector can connect to your MySQL database or not. If not, check if you can ping you MySQL box and check if the user is granted privilege to access locally or remotely.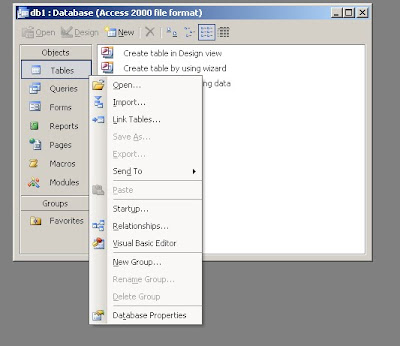 Then select ODBC database() from the "Files of type" and hit on "Link" button
Then select ODBC database() from the "Files of type" and hit on "Link" button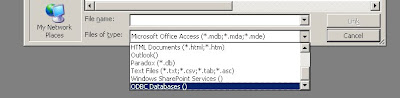 Then it will pop up "Select Data Source" window. Go to "Machine Data Source" tab and click on the desired data source. Let's say you have created 'myData'. Then it pulls up all the table from your defined MySQL database defined in 'myData' data source. Select the table you want to view, edit from the access.
Then it will pop up "Select Data Source" window. Go to "Machine Data Source" tab and click on the desired data source. Let's say you have created 'myData'. Then it pulls up all the table from your defined MySQL database defined in 'myData' data source. Select the table you want to view, edit from the access.